The cremation rate is increasing exponentially in the U.S. now. In 2023 it reached just over 60% nationally, with several states way above this rate. Cremation offers a more affordable disposition option. There is no need for an expensive casket or burial plot. More families are deciding that the expensive of a traditional funeral is no longer an option. And the nature of a more ‘transient’ population and changing attitudes towards tradition, have also bolstered the shift towards cremation as a preferred choice.
To locate a direct cremation provider near you – use our Local Providers Search. All DFS Providers offer a low-cost direct cremation service.

Cremation is such a final disposition that there are certain laws that govern a cremation being conducted. Laws and regulations regarding cremation commonly cover several aspects to ensure the process is conducted appropriately.
Some common aspects covered include:
1. Cremation Authorization: Either an individual must pre-authorize their wish for cremation and pre-sign the authorizations. Or the legal next of kin is required to sign the authorization if a loved one passes. As mentioned, as cremation is so final (leaving no DNA remains), ALL required legal next of kin must sign and be in agreement. So, if there are multiple siblings, all will be required to consent before a funeral director can obtain a permit to cremate.
2. Cremation Permits: Regulations typically require obtaining a cremation permit from the appropriate authorities before conducting a cremation. The permit may include details such as the deceased’s identification, cause of death, and authorization from the next of kin or legal representative. The local County usually issues this permit. Most Counties now charge a fee to issue a cremation permit, which can range from $15.00 to $350.00.
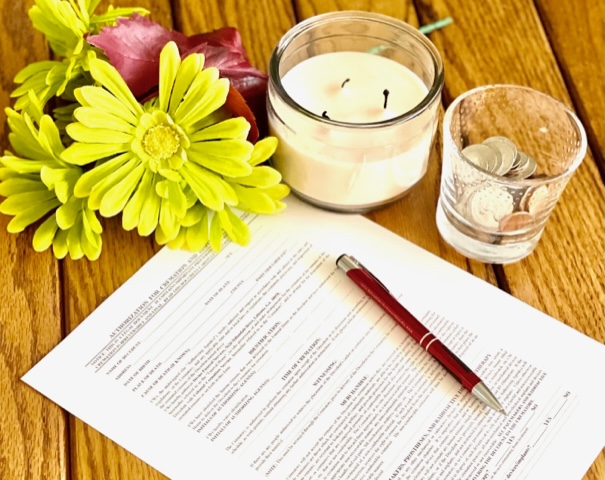

3. Mandatory Wait Period After Death: Many States mandate a minimum wait period after the death occurs before a cremation can be performed. Some states mandate a wait period of 24 hours and some 48 hours. Other states do not mandate a wait period. However, following the process of obtaining authorizations and acquiring permits, death certificates, etc, usually takes between 24-72 hours anyway.
4. Cremation Container Requirements: State law only requires a suitable “rigid, combustible container.” Therefore, most basic cremations are performed using a simple cardboard or pressed wood container. You do not need a casket for a cremation.
5. Environmental and Public Health Standards: Laws often outline specific requirements to ensure that the cremation process is safe for the environment and public health. This may include guidelines for emissions control, proper handling and disposal of medical devices or implants, and the use of environmentally friendly cremation containers.
6. Crematorium Operations: Regulations govern the operation and maintenance of crematorium facilities. This may include guidelines for facility design, equipment maintenance, staff training, and record-keeping procedures. These regulations can vary by State and are usually outlined by the State Funeral Licensing Board.
7. Handling and Disposal of Cremated Remains: Laws often specify the proper handling, transportation, and disposal of cremated remains. This may include guidelines for packaging, labeling, and storing cremated remains, as well as options for their final disposition (such as burial, scattering, or placement in a columbarium).
8. Cultural and Religious Considerations: Some laws may account for specific cultural or religious practices related to cremation. They may provide exemptions or alternative procedures to accommodate these practices, ensuring that the rights and beliefs of individuals are respected.
It’s important to note that the specific aspects covered by laws and regulations regarding cremation can vary between jurisdictions. It is advisable to consult the relevant laws and regulations in your specific area to understand the specific requirements and procedures that apply to cremation.
Visit the State Funeral Planning guides at US Funerals Online to check your individual state legislation on cremation.
To read in more detail about the federal and state laws that govern cremation dispositions and the operation of crematories in the United States, visit Cremation Laws and Arranging a Cremation.